You may have questions about how an electric car works. Whether you already own one or are planning to acquire one, here is everything you need to know about this vehicle.
How does an electric car work?
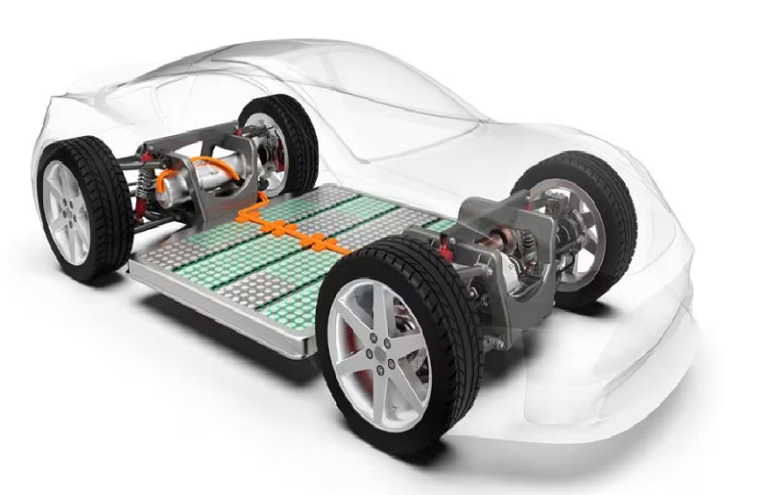
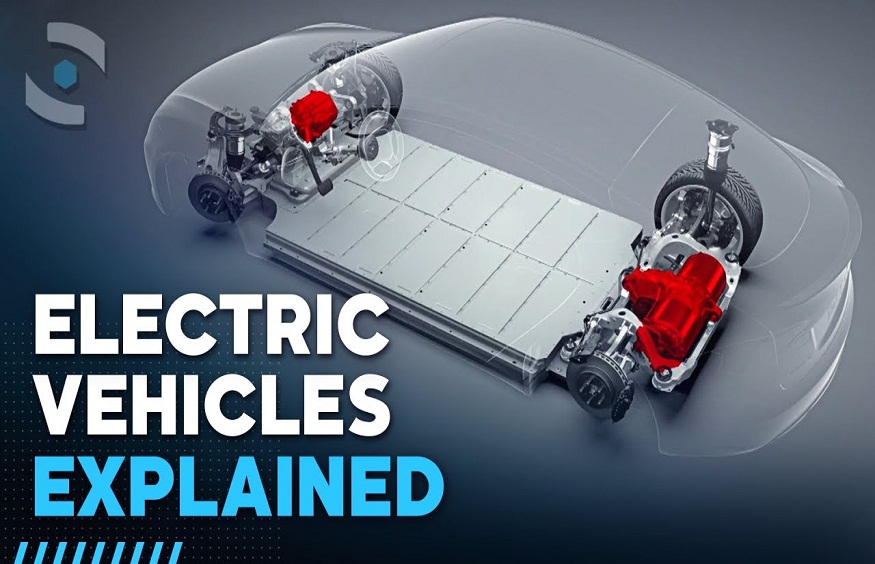
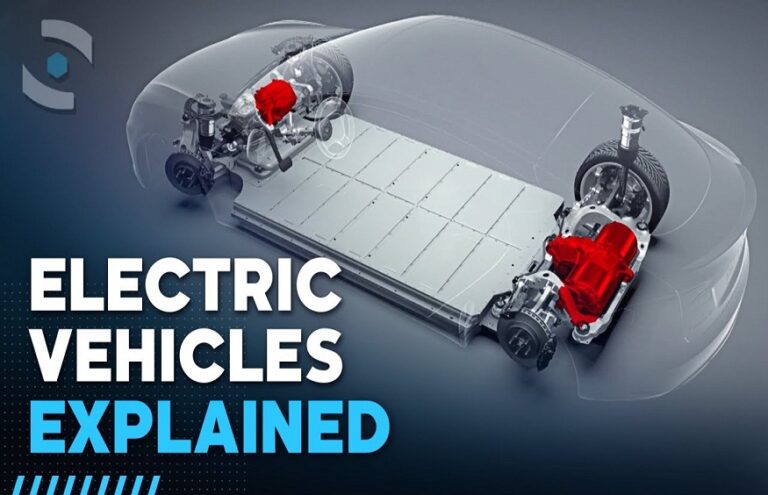
The electric car works with an integrated battery , without gearbox, pistons or transmission belts. Unlike the heat engine, it does not use heat as energy but electricity. The driver plugs in his electric car to recharge it, using an external electrical energy source.
Engine
The electric motor harnesses electromagnetic force to generate movement. The parts that compose it convert electricity into mechanical energy on the physical principle of magnetization. The static part of the machine, the “stator”, thanks to the force of the current, turns the “rotor”, the moving part.
The electric motor is reversible. When it receives electricity, it creates movement; when it is set in motion, it creates electricity.
Furthermore, the motor being somehow directly connected to the wheels, it is a part called a “reducer” which optimizes the rotation speed of the wheel.
Autonomy
If drivers could initially be concerned about the range of electric vehicles, as charging networks multiply, this question becomes less and less of a concern.
In addition, manufacturers are offering electric cars with increasingly greater autonomy . This inormation is naturally present in the vehicle’s maintenance log .
Battery
Thousands of cells make up this centerpiece, in which the current is distributed. These are actually small batteries that are assembled together. Lead-acid batteries, due to their short autonomy and their bulk, have been replaced by lithium batteries, which allow greater autonomy.
The battery stores electrical energy with a chemical solution. Electrons are drawn from this chemical solution, which becomes stable and equilibrium is established between the + and – terminals of the battery. To recharge the battery, electrons must be reinjected into the terminal. This puts the solution back into imbalance and we can again obtain electricity between the + and – terminals.
The amount of energy that the electric battery can store is expressed in kilowatt hours (kWh). The kilowatt (kW) corresponds to the flow of electricity that the battery delivers. Concretely: with a power of 10 kW, a 50 kWh battery can be recharged in around five hours. Why “around”? Because as soon as 80% is reached, the battery automatically reduces the charging speed.
What are the advantages of an electric car?
More and more manufacturers are focusing on electric cars and every year new models are launched. At the same time, a growing number of drivers are switching to electromobility.
The electric car indeed has a large number of advantages:
It respects the environment thanks to the reduction of CO2 emissions: as electric vehicles do not have an exhaust pipe, they do not emit exhaust gases. This significantly reduces air pollution, especially in congested cities. Encouraging the use of electric cars is therefore a lever for municipalities wishing to clean up air quality in order to improve the health and quality of life of their residents.
It allows you to save money in the long term : the cost price of the electric car is attractive compared to gasoline or Diesel. On average, over a year, we can divide the costs of “refuelling” by 5 compared to a thermal car with similar mileage.
It is more reliable than a thermal car : its operation is much simpler. There are fewer parts that wear out, and those that are affected wear out less quickly, especially the brakes, thanks to regenerative braking. Maintaining an electric car allows you to make quite substantial savings compared to thermal vehicles. Same thing for maintaining a hybrid car .
It improves the driving experience : the electric vehicle allows you to pick up speed quickly. Its center of gravity is placed downwards. Its weight is lighter than a traditional vehicle. All this promotes maneuverability, comfort and safety.




















+ There are no comments
Add yours